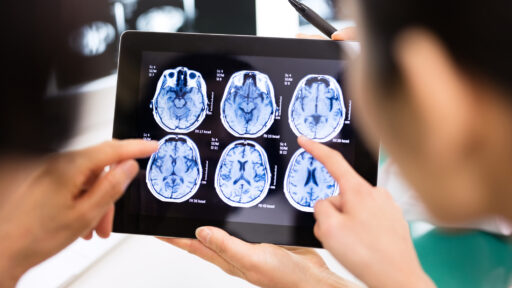
Your brain is the control center of your body. It controls your thoughts, memory, speech, and movement. It regulates the function of many organs. It's part of your nervous system, which also includes your spinal cord and peripheral nerves. The nervous system sends signals between your brain and the rest of the body. Your nerves take in information from your senses and send it to the brain to be processed. Your brain and nerves also communicate to help you move and to control your body's functions.
When the brain is healthy, it works quickly and automatically. But when you have a brain disease, it may affect how well you can function and do your daily activities. Some common brain diseases include:
- Brain tumors, which can press on nerves and affect brain function.
- Degenerative nerve diseases, which can affect many of your body's activities, such as balance, movement, talking, breathing, and heart function. Types include Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
- Encephalitis (inflammation in the brain), which can lead to problems such as vision loss, weakness, and paralysis.
- Genetic brain disorders, which are caused by changes in genes (also called variants or mutations). These disorders can affect the development and function of the brain.
- Strokes, which can cause a loss of brain cells and can affect your ability to think clearly.
- Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), which can affect brain function. They may range from mild to severe. The effects of a TBI may be temporary or permanent.
The symptoms of brain diseases vary widely, depending on the specific problem. In some cases, damage is permanent. In other cases, treatments such as surgery, medicines, or therapies such as physical, occupational, and speech therapies, may cure the disease or improve the symptoms.
Courtesy of MedlinePlus from the National Library of Medicine.
Syndicated Content Details:
Source URL: https://medlineplus.gov/braindiseases.html?utm_source=mplusconnect&utm_medium=service
Source Agency: National Library of Medicine