A benign brain tumor is a group of very slow-growing, abnormal brain tissue cells. Benign brain tumors usually have a distinct tumor border, and rarely spread or invade surrounding brain tissue. Though the word ‘benign’ may sound harmless, a benign tumor located in a vital area of the brain can be life-threatening or fatal without treatment.
Diagnosing a Brain Tumor
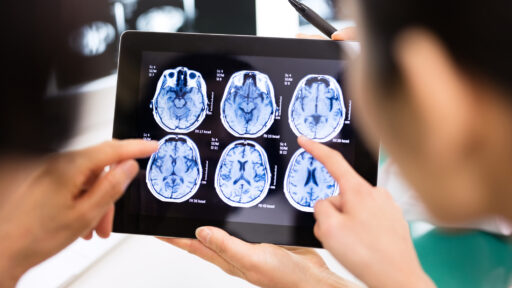
Benign and malignant brain tumors are usually diagnosed by a physician using a patient’s full medical history, a neurological exam and imaging studies, typically using MRI or CT scans. Sometimes a physician may use additional laboratory or blood tests as well as a biopsy. Brain tumors may have a variety of symptoms ranging from a mild headache to dangerous symptoms like those of a stroke. Brain tumors can often mimic symptoms of other problems or diseases, so seek professional medical help if you notice symptoms. Different parts of the brain control different body functions, so symptoms will vary depending on the tumor’s location. Symptoms* of a brain tumor can include:
- Headache
- Double vision, blurred vision or loss of vision
- Seizure
- Memory Loss
- Hearing Loss
- Unsteadiness or loss of balance
- Changes in mood, speech, communication or concentration
* Provided by the American Brain Tumor Association.